Robustness analysis is an approach of filling the gap between analysis and design.
This approach was developed by Ivar Jackobson, but was dropped as one of the unified modelling language (UML).
Robustness analysis is applied during the preliminary design where the designers make assumptions on the design and start thinking of the possible technical solutions towards the problem domain.
It involves analyzing the narrative text of use cases, identifying the first-guess set of objects that will participate in those use cases, and classifying these objects based on the roles they play. Robustness analysis helps you to bridge the gap from Use Cases and Domain Classes, and the model-view-control (MVC) software architecture.
Elements used during robustness analysis
- Entity Object
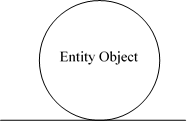
This symbol represents how information is managed in the system. It mainly represents the required functionality within the system.
The entity object mainly encapsulates the business model of the domain.
2. Interface/Boundary Object
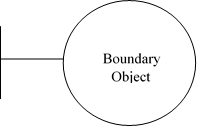
The boundary object symbol represents the interfaces between the actors and the system. The actors are external elements which interact with the system.
3. Control Object

Control object acts as an intermediary between the boundary object and entity object.
This object represents transfer of information or processes within the system.
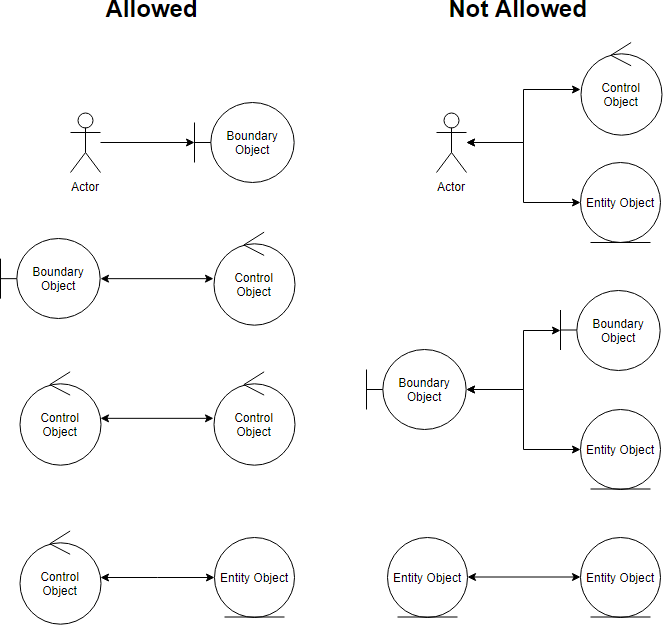
Connection Rules in a Robustness Diagram
Put in consideration that boundary objects and entity objects are nouns while controllers are verbs.
The following are four basic connection rules:
- Actors can only interact or communicate to boundary objects.
- Boundary objects can only communicate to controllers and actors.
- Entity objects can only interact to controllers.
- Controllers can communicate to boundary objects and entity objects, and to other controllers, but not to actors
Steps for creating Robustness Analysis
- Before drawing a robustness diagram you need to have a usecase diagram that displays actors and system’s functionality.
- The wording should be one sentence at a time, and drawing the actors, the appropriate boundary, entity objects and controllers, and the connections among the various elements of the diagram.
- Robustness diagram is only a one diagram you should be able to fit the basic features and all of the alternate features on one diagram.
- Anyone who reviews a robustness diagram should be able to read a course of action in the use case text,and clearly trace associations on the diagram, and see a clear match between text and picture.
Example of a robustness digarm

